By Caroline Clemmons
In the Eastern United States,
riding a coach meant travel from one stage stop to the next, stopping at a
tavern or inn for a meal and perhaps spending the night. In the West and
Southwest, there were not enough established towns. Western travelers had to be
made of grit and determination!
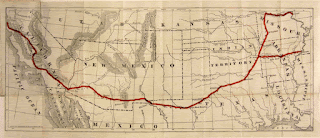
In 1858, John Butterfield
undertook an overland stage line connecting St. Louis and San Francisco by way
of El Paso, Texas. The route also ran through Tucson and Los Angeles, both of
which were only villages of a few hundred residents. A federal contract paid
the stage company $600,000 a year to carry U. S. mail across the continent.
That sum helped subsidize way stations at regular intervals. The company spent
nearly a year getting everything into place to support semi-weekly stagecoach
service.
Butterfield Stage Line Route
When Butterfield’s Overland Mail
Line opened for business on 16 September 1858, the journey between St. Louis
and San Francisco required three weeks of hard traveling—if the weather was good.
Coaches moved all day and all night except for brief intervals at way stations.
The fare did not include the price of meals, which cost an average of a dollar
each three times a day. Passengers had to sleep aboard the coach. These mail
lines were guaranteed to be rugged, but they got the mail through.
Newspaper illustration 1858
Butterfield Stage Coaches
At this time, most coaches set on
springs which provided a bumpy, jostling ride. If passengers were fortunate,
the route included riding in a Concord stagecoach. The first Concord stagecoach
was built in 1827 in Concord, New Hampshire. Abbot Downing Company employed
leather strap braces under their stagecoaches, which gave a swinging motion
instead of the jolting up and down motion of spring suspension. They were known
to be built so solidly they didn’t break, they just wore out.
Concord Stage Coach
Over 700 Concord stagecoaches
were built by the original Abbot Downing Company before it disbanded in 1847.
However, a company by that name was still building coaches, wagons, and carriages, according to their business card of 1898. The coach was noted for its ability
to keep passengers dry while floating across streams and rivers. The swaying
motion caused some passengers to become “seasick”.
In his 1861 book ROUGHING IT,
Mark Twain described the Concord stage’s ride as like “a cradle on wheels.”
Compared to other coaches, the
Concord must have seemed like a smooth-riding luxury sedan would to us.
Mud Wagon
Not all stagecoaches were of one
of these types. Celerity or mud wagons were much lighter and cheaper to build.
They had no springs so they offered a much rougher ride. They were primarily
used on lines where passenger and express traffic was too light to justify the
expense of Concord coaches. Instead of having a heavy wooden top, the celerity
had a light frame structure with thick duck or canvas covering, greatly
reducing the vehicle’s weight. Wheels were set further apart and were protected
by wide steel rims that helped keep the coach from tipping over or the wheels
from sinking in soft sands.
While not as comfortable for
daytime travelers, they were designed for passenger travel at night. Waterman
L. Ormsby, special correspondent to the New
York Herald, described the sleeping accommodations.
“As for sleeping, most of the wagons are arranged so that the backs of
the seats let down and form the length of the vehicle. When the stage is full,
passengers must take turns sleeping. Perhaps the jolting will be found
disagreeable at first, but a few nights without sleeping will obviate that
difficulty, and soon the jolting will be as little of a disturbance as the
rocking of a cradle to a sucking babe. For my part, I found no difficulty
sleeping over the roughest roads, and I have no doubt that anyone else will
learn quite as quickly. A bounce of the wagon, which makes one’s head strike
the top, bottom, or sides, will be equally disregarded, and ‘nature’s sweet
restorer’ found as welcome on the hard bottom of the wagon as in the downy beds
of the St. Nicholas. White pants and kid gloves had better be discarded by most
passengers.”
Celerity/Mud Wagon
sides rolled up
Unlike the classic Concord
stagecoaches, which could be mired in bad weather, mud wagons could travel over
trails and roads during inclement weather. The only protection provided for
passengers against bad weather and dusty roads were the canvas side curtains
which could be rolled down and fastened.
By the way, the word “stage”
meant the place where the horses or mules were changed—staged along the route.
These were spaced every 12 to 20 miles, depending on the terrain, and were
usually operated by a single man living in a small cottage who kept a change of
horses in a barn and/or corral. The stage stopped only long enough for
passengers to stretch their legs while the horses or mules were changed.
Every 50 miles were the “home”
stages, which were usually a couple or family who served meals and could
provide overnight lodging—though sometimes passengers slept on a dirt floor. These
stations also might include a blacksmith and stables. Drivers might be switched
there.
Some coaches had two seats facing
one another. The larger Concord squeezed in a center, forward-facing third seat,
which made passengers very crowded and uncomfortable. Often the third seat had
no back, which must have made retaining balance awkward as the coach swayed
along. Often passengers had to interlock knees due to the crowded interior. Imagine
you were a lady in the 19th century who’d been raised to observe
propriety, and you found yourself on a long coach ride having to lace legs with
a male stranger. Even if he was a perfect gentleman, the situation would be embarrassing.
Here are a set of rules posted by
Wells Fargo in 1888:
1. Abstinence from liquor is
requested, but if you must drink, share the bottle. To do otherwise makes you
appear selfish and unneighborly.
2. If ladies are present,
gentlemen are urged to forego smoking cigars and pipes as the odor of same is
repugnant to the Gentle Sex. Chewing tobacco is permitted but spit WITH the
wind, not against it. (I’d think this would be a given, wouldn’t you?)
3. Gentlemen must refrain from
the use of rough language in the presence of ladies and children.
4. Buffalo robes are provided
for your comfort during cold weather. Hogging robes will not be tolerated and
the offender will be made to ride with the driver.
5. Don’t snore loudly while
sleeping or use your fellow passenger’s shoulder for a pillow; he or she may
not understand and friction may result. (If you’re asleep, how do you control
whether or not you snore and, if you do, how loudly?)
6. Firearms may be kept on your
person for use in emergencies. Do not fire them for pleasure or shoot at wild
animals as the sound riles the horses.
7. In the event of runaway
horses, remain calm. Leaping from the coach in panic will leave you injured, at
the mercy of the elements, hostile Indians, and hungry coyotes.
8. Forbidden topics of
discussion are stagecoach robberies and Indian uprisings.
9. Gents guilty of unchivalrous
behavior toward lady passengers will be put off the stage. It’s a long walk
back. A word to the wise is sufficient. (I love this one!)
To these, the Omaha Herald
in 1877 added cautions to:
Never ride in cold weather with tight boots nor close-fitting
gloves.
When the driver asks you to get out and walk, do so without
grumbling. He will not request it unless absolutely necessary.
Don’t linger too long at the pewter wash basin at the station.
Don’t grease your hair before starting out or dust will stick there in
sufficient quantities to make a respectable ‘tater patch. Tie a silk
handkerchief around your neck to keep out dust and prevent sunburns. A little
glycerin is good in case of chapped hands.
Don’t discuss politics or religion nor point out places on the
road where horrible murders have been committed.
In very cold weather, abstain entirely from liquor while on the
road. A man will freeze twice as quick while under its influence.
Don’t imagine for a minute you are going on a picnic: expect
annoyance, discomfort, and some hardships. If you are disappointed, thank
heaven.
There are many things about the Old West I admire and think I would enjoy. Stagecoach travel is not one of them.
The heroine in my latest release, GENTRY AND THE MAIL ORDER BRIDE, Book 1, Texas Hill Country Mail Order
Bride Series, traveled by stagecoach from Indianola, Texas to Bandera, Texas. Her name is
Heidi Roth, and she had traveled by ship to reach Indianola. This series is of clean, sweet historical western romances, and books are family oriented. They are set in or near the small (fictional) Texas town of Harrigan Springs.
GENTRY is available at: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0B6YN6QHK in e-book and print and is enrolled in Kindle Unlimited.
Here’s the blurb
for
GENTRY AND THE MAIL ORDER BRIDE:
Nothing much riles Gentry McRae. He works hard on the ranch he co-owns
with his immigrant best friend, and is content with his life. He’s proud of all
they’ve accomplished in the ten years since the war. That is, until his partner
dies and leaves a fourth of the ranch to his mail-order bride—and wills the
bride to Gentry.
“Now just a doggone minute, I
don’t plan to marry for years!”
But, a single woman can’t reside on a ranch where four men live without
ruining her reputation. What’s a good man to do, except marry the woman when
she arrives?
Heidi Roth has been spurned for being too plainspoken and too tall. In
addition, her sister constantly makes fun of her for those reasons. That’s
why—with many doubts—she’s willing to travel for months from Germany to Texas
to marry a man who once lived in her town. When she arrives, she learns her
prospective groom is dead, but left a fourth of the ranch he and Gentry owned.
She has serious doubts, but agrees to wed Gentry to protect her reputation.
Sure enough, from the next day, one event after the other happens to complicate
her life and Gentry’s.
Caroline
Clemmons is an award winning and bestselling author of historical and
contemporary western romance. She and her husband live in cowboy country in
North Central Texas, where they are owned by a menagerie of rescued pets.
Sources:
Texas State Historical Association Handbook of Texas
online
http://www.deadwoodmagazine.com/archivedsite/Archives/Stage.htm
http://www.historicthedalles.org/rules_for_stage_travelers.htm
http://www.parks.ca.gov/?page_id=25449
http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/stagecoach.aspx
http://www.wikipedia.com





















.png)














.jpg)